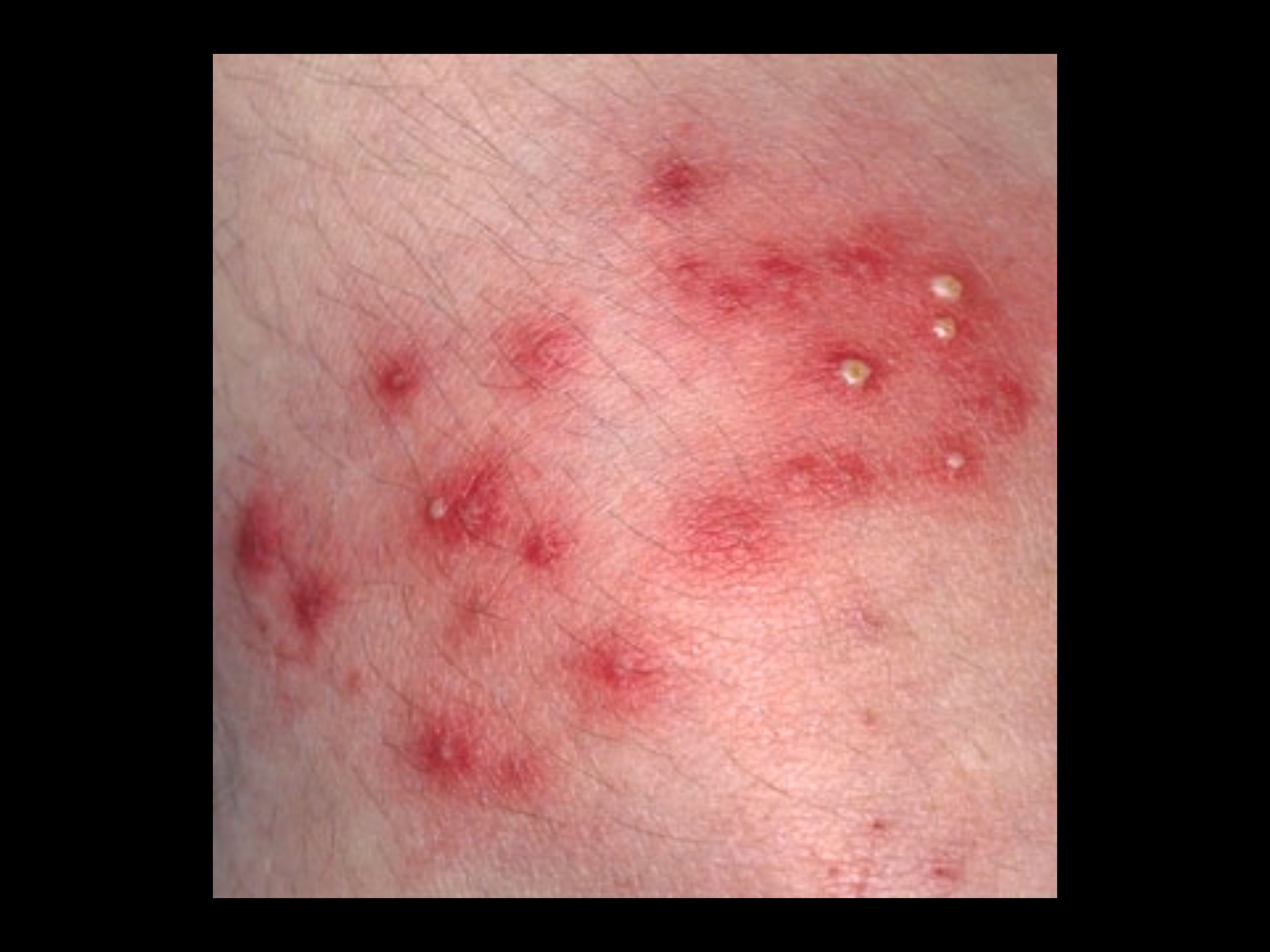
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureaus
TRANSMISSION
Transmitted person-to-person via the hands of health care workers in contact with colonized or infected residents and inadequate hand hygiene between caring for different residents.
COLONIZATION
The presence, growth and multiplication of organism in one or more body sites without observable clinical symptoms. Mostly on skin, open wound or pressure ulcer, sputum and urine. Most common site in both health care workers and residents is the nares (nostrils).
TREATMENT
Vancomycin, an antibiotic, is the drug of choice.
PREVENTION OF MRSA IN ASSISTED LIVING FACILITIES
Residents take part in group activities and therapies that make isolation impractical. For this reason, assisted living communities are treated like community or congregate settings and are considered exempt from hospital isolation guidelines.
Because treatment options for MRSA infections are limited, prevention of infection is key.
For more information on Recommended Protocol and Best Practices for ALF, please contact: Brenda G. Pabellano, BSN, RN, CLNC
PacificLegalNurse@gmail.com